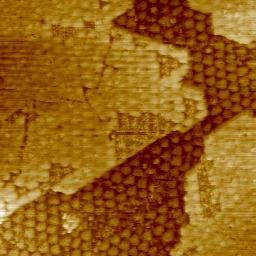
STM - Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
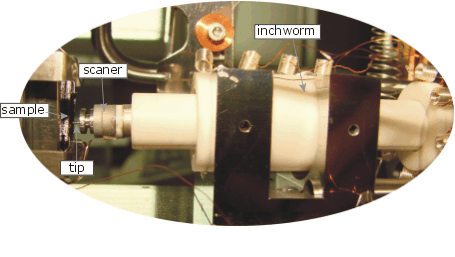
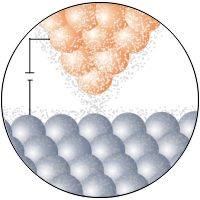
The STM positions an extremely sharp probe tip within a few atomic diameters of the surface. When STM provides bias voltage between the tip and sample a flow of electrons occurs between the tip and the sample. These electrons tunnel from filled states in the surface to empty states in the tip or, if the polarity of bias is reversed, from filled states in the tip to empty states in the surface.
TIP
- electron clouds
tunneling current
bias
SAMPLE
ADVANTAGES of the METHOD in surface science research
the method enables to investigate for conductive samples:
• topography of surfaces with atomic resolution
• surface electronic structure
• nanostructures on surfaces